for Windows*
| Intel® Software Development Products for Intel® Platforms and Technologies | |
| Intel® Visual Fortran Compiler 10.1, Professional and Standard Editions for Windows* |
|
 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| ). |
| Performance |
|
Intel® Visual Fortran Compiler Professional Edition lets you choose the tools that get most out of multi-core processors by combining the Fortran compiler and its built-in optimization, threading, and security capabilities with a highly optimized math library that simplifies the introduction of robust, scalable, multi-threaded math functions.
|
| Advanced Optimization Features |
| Software compiled using the Intel Visual Fortran Compiler for Windows benefits from advanced optimization features, a few of which are explained briefly here, with links to more complete descriptions: |
| Multi-Threaded Application Support, including OpenMP* and auto-parallelization for simple and efficient software threading. | |
| Auto-vectorization parallelizes code to utilize the Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) instruction set architectures (SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, and SSE4) of our latest processors. | |
| High-Performance Parallel Optimizer (HPO)restructures and optimizes loops to ensure that auto-vectorization, OpenMP, or auto-parallelization best utilizes the processor’s capabilities for cache and memory accesses, SIMD instruction sets, and for multiple cores. This revolutionary capability, new in Version 10, combines vectorization, parallelization and loop transformations into a single pass which is faster, more effective and more reliable than prior discrete phases. | |
| Interprocedural Optimization (IPO)dramatically improves performance of small- or medium-sized functions that are used frequently, especially programs that contain calls within loops. The analysis capabilities of this optimizer can also give feedback on vulnerabilities and coding errors, such as uninitialized variables or OpenMP API issues, which cannot be detected as well by compilers which rely strictly on analysis by a compiler front-end. | |
| Profile-guided Optimization (PGO) improves application performance by reducing instruction-cache thrashing, reorganizing code layout, shrinking code size, and reducing branch mispredictions. |
|
| Feature |
Benefit |
| Visual Studio* Support | Developers with Microsoft* Visual Studio* 2005 or 2008 can protect their investment by just plugging in Intel® Visual Fortran. For commercial licensees who don’t use Visual Studio, the Professional Edition includes Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 Premier Partner Edition and, of course, offers command-line usage. The Premier Partner Edition is not included in evaluation or student licenses. Please see the Release Notes for details. |
| VNI’s IMSL* Fortran Library for Windows | The gold standard for numerical computing, the IMSL Fortran Library for Windows provides over 1,000 mathematical and statistical algorithms covering numerical optimization, nonlinear equations, LAPACK, BLAS and more. (Please refer to the IMSL License Agreement ) |
| Compiler and Debugger | |
|
Additional support includes ENUMERATOR, IEEE Floating Point Exception Handling, ALLOCATE extensions, array constructor changes and more to bring your Fortran apps closer to the standard. These join C interoperability features introduced in the last release to make it easier to develop mixed-language applications. |
|
OpenMP raises the parallelism abstraction away from the API, simplifying threading and making code more portable. Previously limited to loop-based data-parallelism, the new 3.0 standard simplifies both data and task parallelism. |
|
Take advantage of new Intel Streaming SIMD Extensions – automatically – through the compiler. No messy low-level coding to get the most from Intel® processors. Resetable for other hosts/targets. |
|
Supports your build by appropriately allocating files to available processors to take advantage of multicore processors and speed you through your edit/compile/debug cycle. |
|
More detailed optimization diagnostics for users who want to use our advanced optimizations to help the compiler do a better job of tuning their applications. The new VTune™ Analyzer 9.1 can filter optimization reports to help guide optimization efforts. |
|
An update of the popular feature from Compaq* Visual Fortran that enables you to create Fortran applications that are usable from the Microsoft .NET* managed code environment. |
|
Find and analyze source file issues. Diagnostics include issues with OpenMP directives, boundary violations, memory corruptions, memory leak, buffer overflow and uninitialized memory. |
| Intel® Math Kernel Library (Intel® MKL) |
|
|
The new architecture provides maximum support for different development environment configurations and processors in a single package. |
|
Link to the version of this layer that matches your development environment and rest assured that Intel MKL will not have threading incompatibilities with the threading in your application. |
|
The DftiCopyDescriptor function has been added for convenience when using the FFTs. The size of statically linked executables calling DFTI has been reduced significantly and complex storage is now available for real-to-real transforms. |
|
The capability to track and/or interrupt the progress of lengthy LAPACK computations has been added. A function called mkl_progress can be defined in a user application, which will be called regularly from a subset of the MKL LAPACK routines. |
|
With performance in mind, all VML functions are now threaded. And a new “Enhance Performance” mode is offered for applications where math-function inaccuracies don’t dominate parameter inaccuracies (e.g., Monte Carlo simulations and media applications). |
|
Improvements include threaded level-3 sparse BLAS triangular solvers and support for all data types (single precision, complex and double complex). |
| Simplified installation |
Streamlined, simplified complete installation for a seamless one-step installation of all components. |
| New Online Support Community |
Our enhanced online community support forums and knowledge base search capabilities help you find answers more quickly. This is in addition to private, password-protected accounts available with Premier Support. Visit the Support Resources pageto learn more! |
| Processor Support |
The addition of support for Intel® Atom™ processors continues to future-proof your investment with assurance of support for each successive generation of processors. That's a key advantage in a world where new hardware platforms come to market with awesome speed. For more details, see the Release Notes. |
|
| This section gives detailed descriptions of the compiler’s advanced optimization features. |
| Multi-Threaded Application Support |
| OpenMP and auto-parallelization help convert serial applications into parallel applications, allowing you to take full advantage of multi-core technology like the Intel® Core™ Duo processor and Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® 2 processor, as well as symmetric multi-processing systems: |
| OpenMP* is the industry standard for portable multithreaded application development. It is effective at fine-grain (loop-level) and large-grain (function-level) threading. OpenMP directives are an easy and powerful way to convert serial applications into parallel applications, enabling potentially big performance gains from parallel execution on multi-core and symmetric multiprocessor systems. |
||
| Auto Parallelization improves application performance on multiprocessor systems by means of automatic threading of loops. This option detects parallel loops capable of being executed safely in parallel and automatically generates multithreaded code. Automatic parallelization relieves the user from having to deal with the low-level details of iteration partitioning, data sharing, thread scheduling, and synchronizations. It also provides the performance benefits available from multiprocessor systems and systems that support Hyper-Threading Technology (HT Technology). |
||
| For more information on multi-threaded application support, visit Intel's Threading Developer Center. | ||
| High Performance, Parallel Optimizer (HPO) |
|
This revolutionary capability, new in Version 10, combines automatic vectorization, automatic parallelization and loop transformations into a single pass which is faster, more effective and more reliable than prior discrete phases. HPO optimizes and restructures program loops to ensure that auto-parallelization, OpenMP, and auto-vectorization occur smoothly in conjunction with each other. HPO’s optimization technology utilizes a unique cost-benefit analysis to make the right optimization decisions for the given program and loop structure. It will perform many transformations such as loop unrolling, peeling, interchange, splitting, etc., as well as other optimizations to ensure the processor’s cache architecture, SIMD instruction set, and multiple cores are well utilized. |
| Automatic Vectorizer |
|
Vectorization automatically parallelizes code to maximize underlying processor capabilities. This advanced optimization analyzes loops and determines when it is safe and effective to execute several iterations of the loop in parallel by utilizing MMX™, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, and SSE4 instructions. Figure 1 is a graphical representation of a vectorized loop that shows four iterations computed with one SSE2 operation. |
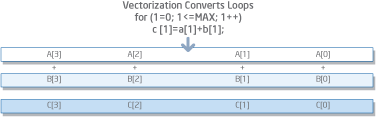 Figure 1. The Vectorizer in action |
|
|
Use vectorization to optimize your application code and take advantage of these new extensions when running on Intel® processors. Features include support for advanced, dynamic data alignment strategies, including loop peeling to generate aligned loads and loop unrolling to match the prefetch of a full cache line. |
||
| Interprocedural Optimization (IPO) |
Interprocedural optimization (IPO) can dramatically improve application performance in programs that contain many small- or medium-sized functions that are frequently used, especially for programs that contain calls within loops. This set of techniques, which can be enabled for automatic operation in the Intel® compilers, uses multiple files or whole programs to detect and perform optimizations, rather than focusing within individual functions.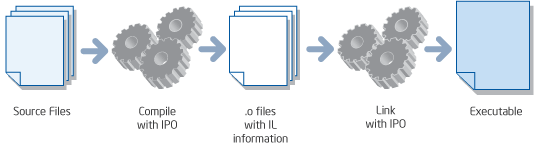 |
|
| Figure 2. The interprocedural optimization process | |
|
| Profile-Guided Optimization (PGO) |
| The Profile-guided optimization (PGO) compilation process enables the Intel Fortran Compiler to take better advantage of the processor microarchitecture, more effectively use instruction paging and cache memory, and make better branch predictions. It improves application performance by reorganizing code layout to reduce instruction-cache thrashing, shrinking code size, and reducing branch mispredictions. PGO is a three-stage process, as shown in Figure 3. Those steps include 1) a compile of the application with instrumentation added, 2) a profile-generation phase, where the application is executed and monitored, and 3) a recompile where the data collected during the first run aids optimization. A description of several code size influencing profile-guided optimizations follows:
|
||||||
 |
||||||
| Figure 3. Profile-guided optimization |
|
| Standards Compliance and Broad Compatibility |
|
The Intel® Visual Fortran Compiler is designed to work with Microsoft development products and depends on certain components of these. It integrates with Microsoft Visual Studio* 2005, as well as Visual Studio .NET* 2003, and provides expanded 32-bit and 64-bit multi-core processor support. The Intel® Visual Fortran Compiler 10.0 for Windows fully supports the Fortran 95 language standard, as well as the previous standards Fortran 90, Fortran 77 and Fortran IV. It also includes many features from the Fortran 2003 language standard, as well as numerous popular language extensions. Significant supported language extensions include: |
| Quadruple precision REAL data type REAL(16) | |
| STRUCTURE, RECORD, UNION, MAP syntax for user-defined types | |
| Directives and functions to enhance mixed-language application development | |
| Binary stream I/O | |
| For a complete list of language features, see the product documentation. The Intel Visual Fortran Compiler 10.0 for Windows also enhances programmer productivity with features such as: |
|
| Run-time array and string bounds checking | |
| Cross-file procedure interface checking | |
| Run-time uninitialized variable detection | |
| Error traceback with file name and line number | |
| The compiler also features extensive compatibility with Compaq Visual Fortran* including language extensions, predefined modules, and library routines. | |
 |
Next-generation data-intensive application developers benefit from dramatic performance optimizations using the Intel compilers to decrease latency and processing times, while also allowing software architects to add additional features without unacceptable impacts to performance. | |
 |
Scientific, research, and related applications benefit from fast compile times, high-performance execution, and solid technical support. Numerically intensive software can make excellent use of the parallelism in Intel processor-based platforms. | |
|
|
This section provides system requirements to develop applications for three different hardware platforms, which are described below. |
|
Architecture Terminology IA-32 architecture - IA-32 Architecture refers to systems based on 32-bit processors generally compatible with the Intel Pentium® II processor, (for example, Intel® Pentium® 4 processor or Intel® Xeon® processor), or processors from other manufacturers supporting the same instruction set, running a 32-bit operating system. Intel® 64 architecture - Intel® 64 Architecture refers to systems based on IA-32 architecture processors which have 64-bit architectural extensions, for example, Intel® Core™2 processor family or Intel® Xeon® processor), running a 64-bit operating system such as Microsoft Windows XP* Professional x64 Edition or Microsoft Windows Vista* x64. If the system is running a 32-bit version of the Windows operating system, then IA-32 architecture applies instead. Systems based on the AMD* Athlon64* and Opteron* processors running a 64-bit operating system are also supported by Intel compilers for Intel® 64 architecture applications. IA-64 architecture - Refers to systems based on the Intel® Itanium® 2 processor running a 64-bit operating system. Native and Cross-Platform Development The following table describes the supported combinations of compilation host (system on which you build the application) and application target (system on which the application runs). |
| Host \ Target | IA-32 architecture | Intel® 64 architecture | IA-64 architecture |
| IA-32 architecture | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Intel® 64 architecture | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| IA-64 architecture | No | No | Yes |
| This section provides system requirements to develop applications for various hardware platforms: | |
| Requirements to develop applications to run on systems with IA-32 or IntelR 64 architecture-based processors or AMD processors | |
| Requirements to develop applications to run on systems with IA-64 architecture-based processors (Intel® Itanium® processors) | |
| Target system requirements to run applications | |
Requirements to develop applications to run on systems with IA-32 or Intel® 64 architecture-based processors or AMD processors |
|
| Host Software Requirements | |||||||||||
| Operating System |
|
||||||||||
| Other Software |
|
||||||||||
Requirements to develop applications to run on systems with IA-64 architecture-based processors (Intel® Itanium® processors) |
| Host Hardware Requirements | ||||||||
| Component | Minimum | Recommended | ||||||
| Processor (any one required) |
|
|
||||||
| RAM |
|
|
||||||
| Disk Space |
|
|
||||||
| Host Software Requirements | |||||||||
| Operating System |
|
||||||||
| Other Software |
|
||||||||
| Target system requirements to run applications | |||||||
| Platform | Requirements | ||||||
| IA-32 architecture-based systems |
|
||||||
| Intel 64 architecture-based systems |
|
||||||
| IA-64 architecture-based systems |
|
||||||
|
|||
|
Adobe* Reader* version 7.0 or later is required to view some of the reference documentation. |
|||
|
It is the responsibility of application developers to ensure that the machine instructions contained in the application are supported by the operating system and processor on which the application is to run. |
| Intel provides both the tools and support to enhance the performance, functionality, and efficiency of software applications. |
| Compatible with leading Windows* and Linux* development environments, Intel® Software Development Products are the fastest and easiest way to take advantage of the latest features of Intel processors. Intel Software Development Products are designed for use in the full development cycle, and include Intel® Performance Libraries, Intel® Compilers (C++, Fortran for Windows, Linux, and Mac OS* X), Intel® VTune™ Analyzer, Intel® Threading Tools and Intel® Cluster Tools. |
| The Intel® Premier Support Web site provides expert technical support for all Intel software products, product updates and related downloads. For additional product information visit: www.intel.com/software/products. |
| Intel, the Intel logo, and VTune are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries. |
| *Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others. |
| Copyright © 2007, Intel Corporation |